
-
Apexlink
Real Estate
-
DLS
General Insurance
-
DMV
Government
-
Entiger
Fintech
-
GIS Mapping
Gas & Petroleum
-
HMS
Employee Benefit
-
HAWA
Government
-
Harley
Community
-
IHG
Hotel & Tourism
-
Sparkseeker
Humane Tech
-
Track Ninja
Sports
-
Response Vision
Disaster Management
- Artificial Intelligence
- Application Services
- Automation Services
- Cyber Security
- Chatbot Experts
- Data Analysis
- Data Warehouse Services
- Machine Learning
- Digital Commerce Services
- Digital Transformation
- Infrastructure Service
- IT Support
- IT Consulting
- IT Outsourcing
- IOS Development
- Android Development
-
Cross Platform Development
-
Gaming App Development
This innovative technology’s discovery goes back to 1960’s and the evolution of cloud computing has seen multiple stages. We have come so far, and its equally important to know about how and when did cloud computing start empowering enterprises along with the entire history of cloud computing, before we dive into top trends in the future.
We have seen it, heard it, and done it. But, do we know what it is? We have been using cloud computing unknowingly through Gmail and Google docs, yet we never thought that these were cloud computing services.

What is Cloud Computing technology?
Cloud computing is a technology that puts your entire computing infrastructure in both hardware and software applications online. It uses the internet, remote central servers to maintain data & applications. Gmail, Yahoo mail, Facebook, Hotmail, Orkut, etc are all the most basic and widely used examples of cloud computing. One does not need his own PC or laptop to check some stored mail/data/photos in the mailbox but any computer with an internet connection since the data is stored with the mail service provider on a remote cloud. The technology, in essence, is a geographical shift in the location of our data from personal computers to a centralized server or ‘cloud’. Typically, cloud services charge its customers on a usage basis. Hence it is also called Software as a Service (SaaS). It aims to provide infrastructure and resources online in order to serve its clients; Dynamism, Abstraction and Resource Sharing.
The term “cloud” was actually derived from telephony. The telecommunication companies offered Virtual Private Network with good quality at affordable prices. The symbol of the cloud represented the demarcation point which was the sole responsibility of the provider. Cloud computing manages servers and network infrastructure management.
Cloud Solution
It has essentially evolved from various computing technologies like grid computing, utility computing, parallel computing, and virtualization. The most recent development of cloud computing has evolved from the Web2.0 technology which caters to web applications that facilitate participatory information sharing, interoperability & user-centred design, etc. Examples of Web 2.0 include wikis, blogs, social networking & video sharing.
History of Cloud Computing
Let’s have a quick walkthrough of cloud computing history and evolution all these years-
1960’s
One of the renowned names in Computer Science, John McCarthy, enabled enterprises to use expensive mainframe and introduced the whole concept of time-sharing. This turned out to be a huge contribution to the pioneering of Cloud computing concept and establishment of Internet.
1969
With the vision to interconnect the global space, J.C.R. Licklider introduced the concepts of “Galactic Network” and “Intergalactic Computer Network” and also developed Advanced Research Projects Agency Network- ARPANET.
1970
By this era, it was possible to run multiple Operating Systems in isolated environment.
1997
Prof. Ramnath Chellappa introduced the concept of “Cloud Computing” in Dallas.
1999
Salesforce.com started the whole concept of enterprise applications through the medium of simple websites. Along with that, the services firm also covered the way to help experts deliver applications via the Internet.
2003
The Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), that allows running of multiple virtual guest operating systems on single device, paved way ahead for other huge inventions.
2006
Amazon also started expanding in cloud services. From EC2 to Simple Storage Service S3, they introduced pay-as-you-go model, which has become a standard practice even today.
2013
With IaaS, (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), the Worldwide Public Cloud Services Market was totalled at £78bn, which turned out to be the fastest growing market services of that year.
The evolution of cloud computing can be bifurcated into three basic phases:
- The Idea Phase- This phase incepted in the early 1960s with the emergence of utility and grid computing and lasted till pre-internet bubble era. Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider was the founder of cloud computing.
- The Pre-cloud Phase- The pre-cloud phase originated in 1999 and extended to 2006. In this phase the internet as the mechanism to provide Application as Service.
- The Cloud Phase- The much talked about real cloud phase started in the year 2007 when the classification of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS development got formalized. The history of cloud computing has witnessed some very interesting breakthroughs launched by some of the leading computer/web organizations of the world.
Security Aspects Strengthened In Further Years
The further years witnessed development of basic cloud features, while making security to be a rising concern. This fast-growing service was secured from theft, accidental deletion, and data leakage concerns.
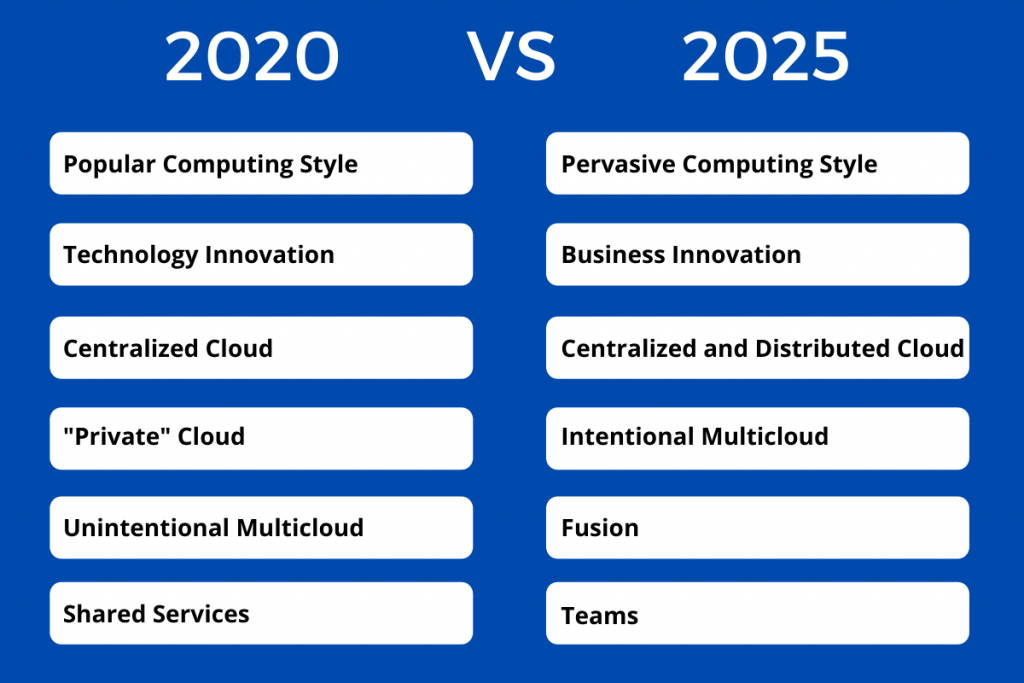
Cloud Shifts from 2020- 2025
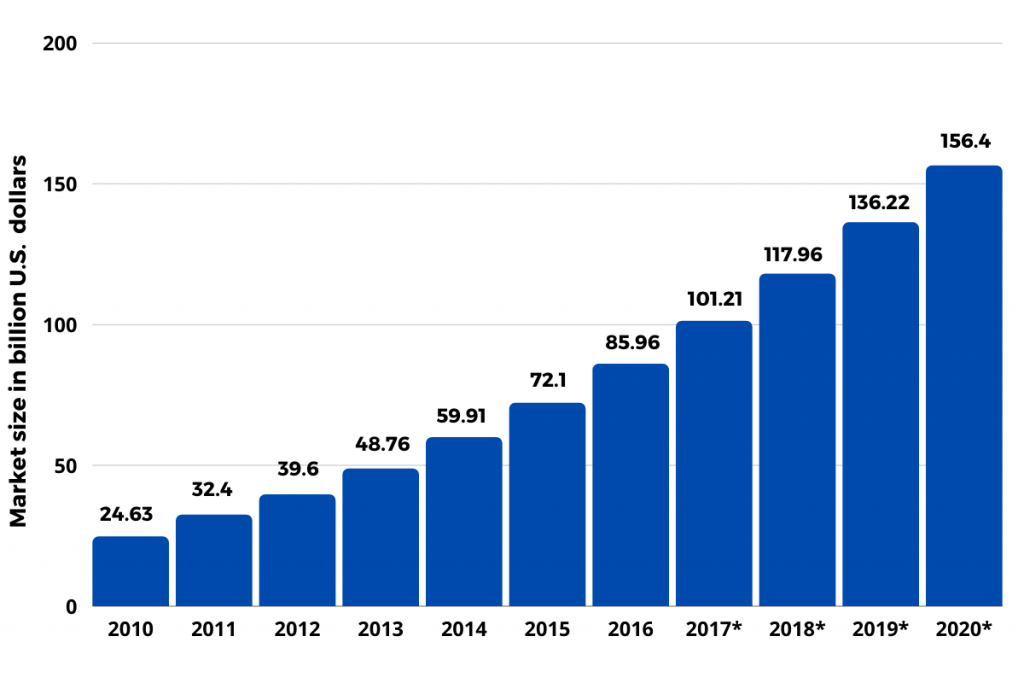
Varieties of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is classified under various heads. On the basis of the type, usage & location, it is classified under the following head:
- Public Cloud- When a cloud is available to the general public on a pay-per-use basis, that cloud is called a ‘Public Cloud’. The customer has no visibility over the location of the cloud computing infrastructure. It is based on the standard cloud computing model. Examples of public cloud are Amazon EC2, Windows Azure service platform, IBM’s Blue cloud.
- Private Cloud- The internal data centers of business organizations which are not made available to the general public are termed as a private cloud. As the name suggests, the private cloud is dedicated to the customer itself. These are more secured as compared to public clouds. It uses the technology of virtualization. A private cloud is hosted on the company’s own servers. Example of private cloud technology is Eucalyptus and VMware.
- Hybrid Cloud- A combination of private and public cloud is called a hybrid cloud. Companies use their own infrastructure for normal usage and hire the cloud at events of heavy network traffic or high data load.
Cloud Computing Trends – Empowering the future of Public Cloud
The estimated spending on Public Cloud Services is foreseen to surpass $500 Billion by 2023. The upcoming trends in cloud computing are going to empower industries with multiple cloud offerings and accelerated growth.
As a result, the cloud adoption will grow by 22.8% of all enterprise IT sending.

“The pandemic served as a catalyst for rapid cloud adoption and digital innovation in 2020, especially to empower remote work, collaboration and digitalization for hybrid work models”.
Cloud Ubiquity- Setting the Stage for Distributed Cloud Models
With its proven scalability, resiliency, speed and flexibility, the cloud environments are reaching ubiquitous stages. The use of multicloud, Hybrid and edge environments are giving push to wireless communications advancements naming 5G R17 and is transforming industries experiences such as healthcare, mobile banking experiences and more.
Distributed Cloud Models
- Cloud Business Process Services (BPaaS)
- Cloud Application Infrastructure Services (PaaS)
- Cloud Application Services (SaaS)
- Cloud Management and Security Services
- Cloud System Infrastructure Services (IaaS)
- Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
Cloud Storage Capacity
As cloud services progressively turn into an essential part of doing business, we anticipate data storage to develop exponentially in the coming time. To achieve this, organizations will arrange more data centers online with bigger capacity storage equipment.
While the owners of data centers are going to increase the available storage, forward-thinking organizations will have the capacity to use that space to fulfill their requirements. For instance, organizations that work with big data will utilize this expanded space to store large data indexes or sets and perform analytics on them, and reap valuable insights into areas, for example, client behavior, human frameworks, and strategic financial investment. For small private companies, expanded storage capacity implies that 2025 will give custom or bespoke storage alternatives at far lower costs than were accessible in 2020.
Regional Cloud Ecosystems
The creation of vertical and regional cloud systems, along with data services is driving is driving many industries to whole new levels, especially the financial and public sectors. Since the ultimate goal is to reduce points of failure and lock-ins with outsourced cloud providers.
The companies looking to sustain their own platform ecosystems are going to leverage the platforms created in other regions. These organisations are resorting to regulations that can help maintain sovereignty and control. The initiatives such as GAIA-X development in European countries is increasing gaining popularities as it turns out to be solutions for politicians, tech providers and academia concerns.
“Carbon-Intelligent” Cloud
The climate change mitigation is a harsh reality today and is going to leave a huge impact on businesses all over the world. The Cloud providers have come up with sustainable solution by incorporating aggressive carbon-neutral corporate goals. This is further leading to problems and challenges for I&O (Infrastructure and operations) leaders as the industries are demanding “green” initiatives.
Better Internet Quality
The measure of data produced and stored around the globe is expected to grow enormously by 2025, and the purchasers will also expect better and quicker connections from network providers.
Improved network speed will increase the buyer’s desires for exceedingly responsive, quick loading services and applications. Keen entrepreneurs will move rapidly to re-examine and overhaul their SaaS, PaaS, and websites to be more responsive. The IOE and IOT will additionally take advantage of the faster network by allowing companies in this space to receive and deliver data efficiently in real time.
The IoE will become the dominant focal point
In 2020, IoT and AI played a stellar part in the tech world. While industry experts expect that IoT will see its own development, nonstop innovations in the real-time data analytics and the developing technology cloud computing are set to push the IOE to fore in 2025. IoE depends on the machine-to-machine interaction, process, and data and how people speak with everything in their condition. Cloud computing will play a major role as the IoE forms into complex frameworks aimed at simplifying all interactions.
For people, this implies we will have the capacity to interact cleverly with each gadget in a network—simply like IoT.
IoE will also furnish organizations with more insight into how shoppers relate to their services or products, customer care units, and each other. This information would then be used in numerous ways, including simplifying client experience through automation and the utilization of savvy robots.
Security challenges and the cloud
Because cyber-attacks are turning out to be more complex, security examiners in government, private and public areas will also need to become more refined and auspicious in their techniques for recognizing and preventing attacks. Organizations will recognize the need for investing in tools like security data, event management, and malware detection frameworks as crucial defense mechanisms for digital security. The role of cloud computing services can also play a role here, with managed security service providers offering strong services to organizations that couldn't generally execute full security measures.
Wrapping up
Finding and adopting the latest trends in cloud computing is crucial for organizations at all levels. From a technology that was initially used for cost savings and efficiency, the cloud has turned into an innovation powerhouse. While the future of cloud computing can be difficult to predict, it is sure that the technology will continue having a significant effect on the business process.







 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
 Blockchain
Blockchain Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Services
Infrastructure
Services Metaverse
Metaverse QA
Automation
QA
Automation UI/UX
UI/UX








