
-
Apexlink
Real Estate
-
DLS
General Insurance
-
DMV
Government
-
Entiger
Fintech
-
GIS Mapping
Gas & Petroleum
-
HMS
Employee Benefit
-
HAWA
Government
-
Harley
Community
-
IHG
Hotel & Tourism
-
Sparkseeker
Humane Tech
-
Track Ninja
Sports
-
Response Vision
Disaster Management
- AI/ML Services
- Application Services
- Automation Services
- Cyber Security
- Chatbot Experts
- Data Analysis
- Data Warehouse Services
- Digital Commerce Services
- Digital Transformation
- Infrastructure Service
- Low Code/No Code
- Managed IT Services
- IT Support
- IT Consulting
- IT Outsourcing
- Mobile App Development
- IOS Development
- Android Development
- Cross Platform Development
- Gaming App Development
- Software Development
- System Design & Architecture
- Testing Services
- Web Development
Accelerators
POCs and Products
Data is the new oil.
Almost every business out there is focused on collecting as much data as possible; however, it is important to note that, just like oil, data in its raw form is of little use. It is vital to analyze and process the data in a manner that helps get the most out of it.
Data analytics is the means that allows you to analyze raw data and extract meaningful, actionable insights from it. These insights can be implemented for better decision-making and to steer your business toward tremendous success.
In this comprehensive guide to data analytics, we’ll introduce you to the concept of data analytics, its importance and ability to influence business decisions, types of data analytics, and more.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics is a form of business intelligence typically used to address and solve specific organizational problems and challenges. Data analysts extract raw data and interpret it to come up with suggestions and recommendations on how the organization should proceed. These data-backed insights are capable of helping generate great results.
Relevant data can help you get actionable insights concerning almost all aspects of a business – from understanding how a particular customer behaves to what drives most conversions – there’s so much you can do when you utilize data analytics.
The process also provides a method for comprehending past events and forecasting future patterns and actions, enabling informed choices instead of relying on conjecture. With the knowledge gleaned from data analysis, companies, and organizations have a more precise grasp of their customer base, sector, and business, leading to more effective decision-making and strategic planning.
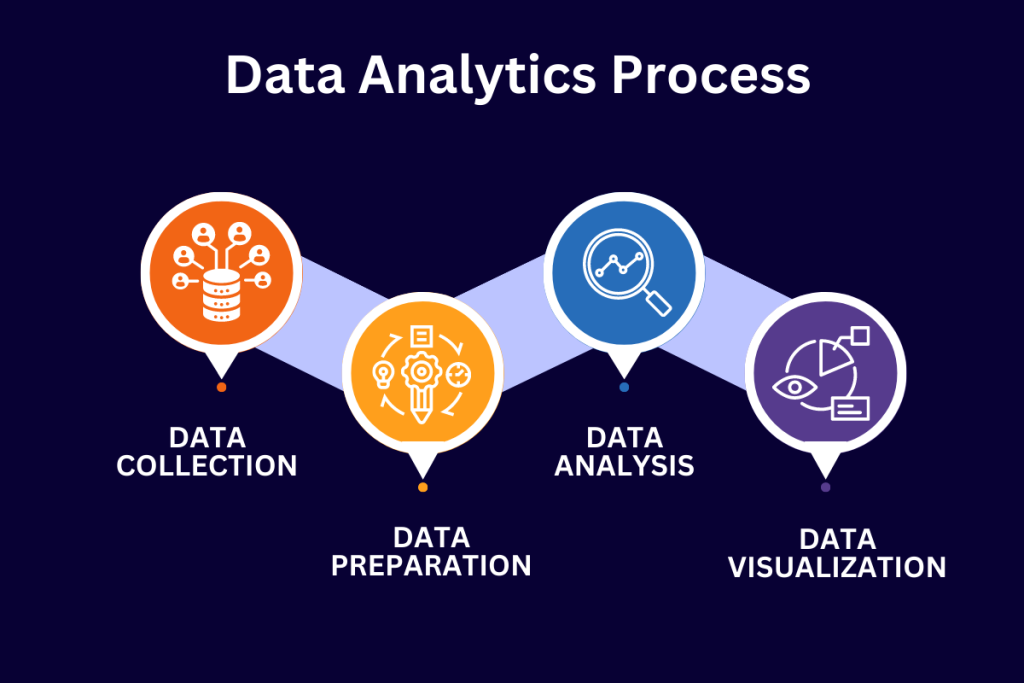
Data Analytics Process
The data analytics process is a systematic approach to analyzing data that involves four main stages:
- Data collection
- Data preparation
- Data analysis
- Data visualization
Here is a brief overview of each of these stages:
- Data Collection: The first step in the data analytics process is to collect the data for analysis. This may involve gathering data from various sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and other sources. Depending on the scope of the analysis, data can be collected from internal or external sources.
- Data Preparation: Once the data has been collected, it needs to be prepared for analysis. This may involve cleaning the data to remove any errors or inconsistencies, transforming the data into a format that is suitable for research, and integrating the data from different sources. This step is crucial, as the quality of the analysis is heavily dependent on the data quality.
- Data Analysis: As soon as the data has been collected and prepared, it is time to analyze the data. This involves using various statistical and machine-learning techniques to identify data patterns, relationships, and trends. This step may include using software tools and programming languages like Python, R, or SQL to perform the analysis.
- Data Visualization: The final step in data analytics is visualizing the analysis results. This may involve creating charts, graphs, and other visual representations of the data to help communicate the insights and trends to others. The goal of data visualization is to make the analysis accessible and understandable to decision-makers who may not have a background in data analytics.
What are the types of data analytics?
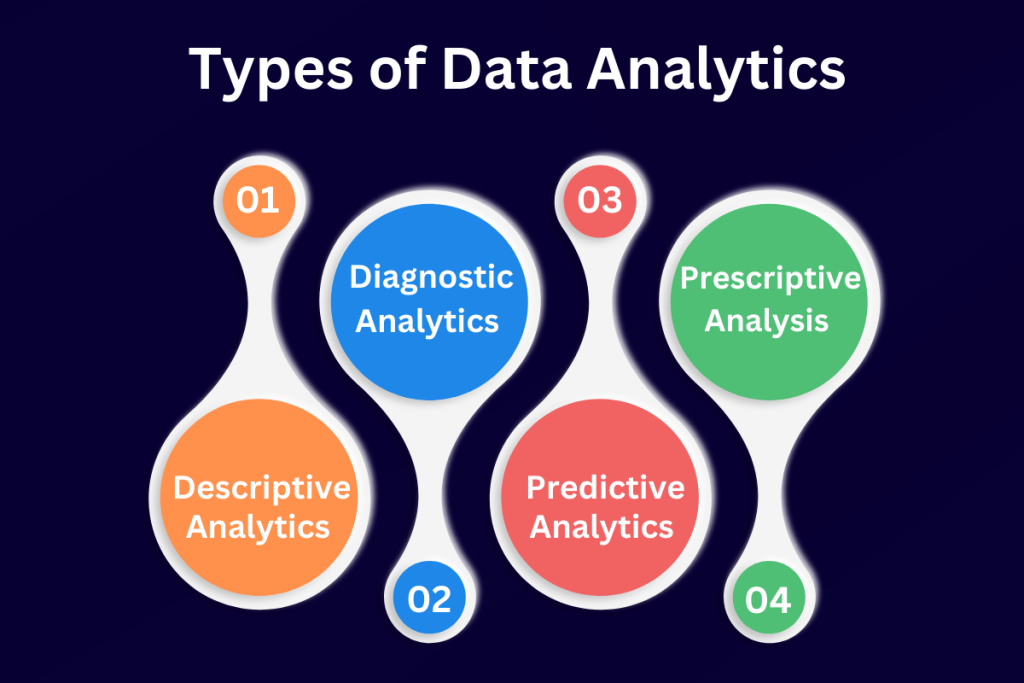
Data analysis is primarily categorized into four main types –
- Descriptive Analytics
- Diagnostic Analytics
- Predictive Analytics
- Prescriptive Analytics
Let’s take a look at each of these:
- Descriptive Analytics: Descriptive analytics is a type of data analysis that focuses on describing what has happened in the past. It involves summarizing and visualizing historical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. Descriptive analytics is used to gain insights into past events, and it’s often used to support decision-making by providing context and a deeper understanding of what has happened.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Diagnostic analytics is a type of data analysis focusing on understanding why something happened in the past. It involves drilling down into the data to identify a problem’s root cause or explain a particular trend or pattern. Diagnostic analytics is often used with descriptive analytics to provide a complete understanding of past events.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics is a type of data analysis focusing on predicting future events based on past data. It uses statistical and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and relationships in historical data and then uses that information to make predictions about what is likely to happen in the future. Predictive analytics is used to identify trends, make forecasts, and develop models that can be used to support decision-making.
- Prescriptive Analysis: Prescriptive analysis is a type of data analysis that focuses on recommending specific actions that should be taken to achieve a desired outcome. It involves using advanced algorithms and models to evaluate different scenarios and to determine the best course of action. A prescriptive analysis is often used with predictive analytics to identify the best course of action based on predicted outcomes. It is a powerful tool for decision-making because it not only determines the likely effects of different scenarios but also provides a recommended course of action based on those outcomes.
Why is data analytics important?
Data analytics is important because it allows individuals and organizations to derive insights and make informed decisions based on data. By analyzing large volumes of data, data analytics can uncover patterns and trends that might go unnoticed, enabling businesses to optimize their operations, improve their products and services, and identify new opportunities. It can also help individuals and organizations make more data-driven decisions, reducing the risk of costly mistakes and increasing the likelihood of success.
Overall, data analytics is crucial for anyone seeking to better understand the world around them and make smarter decisions based on objective evidence.
What’s the difference between data analytics and data science?
Many people in the technology domain use the terms’ data science’ and ‘data analytics’ interchangeably. Not only both of these are entirely different career domains, but they also impact a business or an organization in completely different ways.
To understand the difference between the two, we must look at the roles and responsibilities of a data analyst and a data scientist.
A data analyst analyzes data to identify patterns, trends, and insights to inform business decisions. Their responsibilities may include data cleaning, data visualization, and creating reports. They often work with structured data and use tools like SQL, Excel, and Tableau.
On the other hand, a data scientist typically has a broader skill set that includes statistics, machine learning, and programming. They may work with structured and unstructured data and use tools like Python and R. Their responsibilities may include developing predictive models, designing experiments, and developing data pipelines.
While there is an overlap between the two roles, data scientists typically have more advanced skills and work on more complex problems. Data analysts may work under the supervision of data scientists or as part of a larger team that includes data scientists.
Is data analytics a promising career?
Yes, data analytics can be an outstanding career. With the growing importance of data in business and other fields, there is a high demand for skilled data analysts who can help organizations make sense of their data and use it to drive decisions.
A career in data analytics can be financially rewarding, with many job opportunities offering competitive salaries and benefits. In addition, data analytics can be a fulfilling career for those who enjoy working with data, solving problems, and finding insights that can make a real impact. As with any profession, success in data analytics requires a strong work ethic, a commitment to continuous learning, and the ability to communicate insights effectively to stakeholders.
Data Analytics in Business
Data analytics can benefit businesses by allowing them to make data-driven decisions and gain valuable insights into their operations, customers, and market trends. By analyzing data, companies can identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement, which can help them to optimize their processes, increase efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately boost profitability.
Data analytics can also help businesses better understand their customers, including their preferences, behavior, and needs, which can inform marketing strategies and product development. However, to effectively utilize data analytics, businesses need the right tools and expertise in place, as well as a solid understanding of how to interpret and act on the insights provided by the data.
Future of Data Analytics
The future of data analytics is exciting, with emerging trends such as big data, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things poised to transform how businesses use data. These trends will bring new opportunities and challenges, and businesses must adapt to stay competitive. They will need to invest in new technologies, develop new skills, and remain vigilant about the ethical implications of data analytics.
The Final Note
In conclusion, data analytics is an essential tool for businesses and organizations as it helps them make informed decisions based on data. The process of data analytics comprises four main stages: data collection, data preparation, data analysis, and data visualization. Data analytics is divided into four types, descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. It differs from data science as data analytics mainly focuses on using historical data to provide insights for better decision-making. In contrast, data science emphasizes mathematical and statistical techniques for exploring data.
Therefore, data analytics is a must-have tool for every organization seeking to improve its products and services, reduce the risk of costly mistakes, and increase the likelihood of success.







 Blockchain
Blockchain Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Services
Infrastructure
Services Metaverse
Metaverse QA
Automation
QA
Automation UI/UX
UI/UX







