
-
Apexlink
Real Estate
-
DLS
General Insurance
-
DMV
Government
-
Entiger
Fintech
-
GIS Mapping
Gas & Petroleum
-
HMS
Employee Benefit
-
HAWA
Government
-
Harley
Community
-
IHG
Hotel & Tourism
-
Sparkseeker
Humane Tech
-
Track Ninja
Sports
-
Response Vision
Disaster Management
- AI/ML Services
- Application Services
- Automation Services
- Cyber Security
- Chatbot Experts
- Data Analysis
- Data Warehouse Services
- Digital Commerce Services
- Digital Transformation
- Infrastructure Service
- Low Code/No Code
- Managed IT Services
- IT Support
- IT Consulting
- IT Outsourcing
- Mobile App Development
- IOS Development
- Android Development
- Cross Platform Development
- Gaming App Development
- Software Development
- System Design & Architecture
- Testing Services
- Web Development
Digital twin technology has undergone a beautiful transformation to become an emergent reality from a science-fiction concept. The technology has altered several industries and apparently unlocked unprecedented prospects in optimization, innovation, and strategy. DTT connects the physical & digital worlds by constructing virtual replicas of physical entities to enable real-time data analysis, simulation, and prediction. Now, let's look at the strategic opportunities that digital twin technology offers to businesses, gaining a thorough understanding of its uses, benefits, & future potential.
At Seasia Infotech, we take pride in leading this change. Our digital twin solutions give industries a full, up-to-date picture of their operations. This helps businesses make smarter choices based on data, which boosts productivity and cuts costs.
What is Digital Twin Technology?
What is Digital Twin Technology?
Digital twins are virtual versions of their physical counterparts that might take the shape of an object, process, or system. Driven by data sensors, IoT, & artificial intelligence, these digital twins replicate real time data into simulated environments. This also enables businesses to monitor, test, & analyze these 'digital twins' for them to make smarter decisions.
Strategic Possibilities of Digital Twin Technology
There are numerous strategic possibilities digital twin technology brings to the table, some hidden in plain sight. Most common ones include:
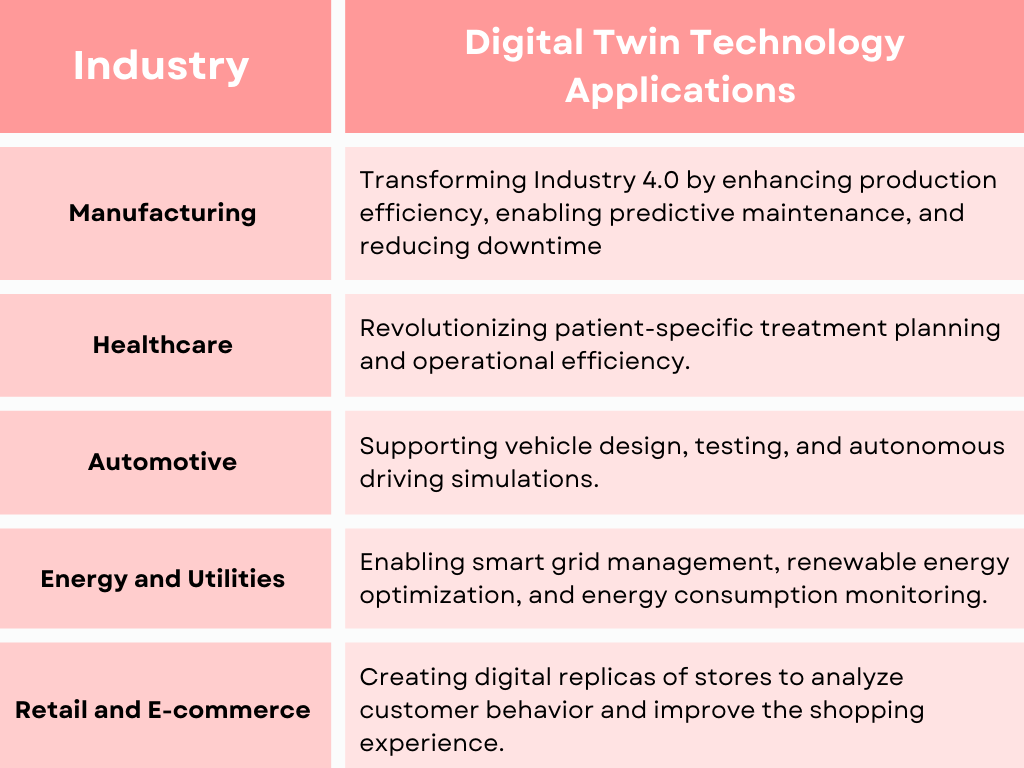
Enhanced Product Development
Digital twins allow businesses to design, test, and optimize products in a virtual environment before manufacturing them. This reduces costs, shortens development cycles, and improves product quality. For example, automotive manufacturers use digital twins to test vehicle aerodynamics or engine performance in virtual settings. Similarly, in the consumer electronics domain, companies simulate user interactions and stress-test devices virtually.
Optimized Operations and Maintenance
By mirroring physical systems, digital twins enable predictive maintenance. This allows businesses to foresee potential failures, minimize downtime, and reduce operational costs. In manufacturing plants, digital twins help monitor equipment health and predict maintenance needs. DTT has been making a mark in the energy sector too. Utility companies use digital twins to manage grids efficiently and prevent outages.
Improved Supply Chain Management
Digital twins provide real-time visibility into the supply chain, enabling businesses to anticipate disruptions, optimize logistics, and manage inventory effectively. Inventory management systems powered by digital twins optimize stock levels and reduce wastage in the retail industry. In logistics, shipping companies simulate and optimize delivery routes to ensure timely deliveries.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Businesses can create personalized customer experiences by leveraging digital twins to understand customer behavior and preferences, which is particularly beneficial for the retail and e-commerce industry. Digital replicas of stores allow businesses to test layouts and product placements. Likewise, developers working on projects related to the real estate industry use digital twins to provide virtual walkthroughs of properties.
Urban Planning and Smart Cities
Governments and urban planners use digital twins to model cities, analyze traffic patterns, and optimize energy usage. These models help in creating sustainable and efficient urban spaces. A common example can be Singapore’s virtual twin that is being used extensively to test urban development strategies.
Strategic Decision Making
Digital twins provide real-time insights and predictive analytics, enabling businesses to make informed strategic decisions. From risk management to resource allocation, businesses can simulate scenarios and plan effectively. For instance, hospitals use digital twins to optimize patient flow and resource utilization, and financial institutions simulate economic scenarios to plan investments using this technology.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Digital twins help organizations achieve sustainability goals by monitoring energy consumption, reducing waste, and optimizing resource use. Digital twins are often used to simulate energy-efficient production lines. In construction, architects and engineers use digital twins to design eco-friendly buildings.
Digital Twin Technology Implementation Challenges
Even so, there are specific challenges closely tied to applying the digital twin technology to your needs. These include:
High Initial Costs
The initial investment is another barrier against widespread adoption, as businesses have to integrate multiple technologies, including IoT sensors, Artificial intelligence solution platforms, cloud computing, and advanced analytics tools, each of which incurs significant costs. This financial burden is greatly compounded by maintenance, upgrading, and scaling the technology over time. Depending on business size, these costs can be prohibitive, contributing to delayed adoption.

Data Security Risks
Digital twins gather, analyze, and store large amounts of sensitive business information that makes them appealing targets for cyberattacks. Data breaches are capable of leaking sensitive information such as operational details, product design, and customer behavior. This additional complexity necessitates the implementation of robust cybersecurity controls to secure both the physical systems and their virtual counterparts—a process that can be costly and technically complex. When done poorly or without strong safeguards, businesses can expose proprietary or sensitive data. This is where our cybersecurity services and fraud detection software can address many business concerns.
Complexity
The key challenge lies in the fact that adopting digital twin technologies is indeed a complex task which spans across many domains such as Internet of things, AI, cloud infrastructure, and system integration. It requires putting people with the right skills in the right place to build, oversee, and fine-tune the tech. In addition, seamless integration with existing systems, hardware, and processes may be a big technical challenge. Without the right knowledge and tools, companies can run into delays and inefficiencies. This is where collaborating with a reputable software development company can simplify the process.
Scalability Challenges
Scaling the digital twin from one operation or one application to many operations is where it gets a bit daunting. As the number of connected devices and corresponding data feeds proliferate, real-time responsiveness and accuracy become harder to keep. Scaling up is also a challenge for many organizations due to infrastructure constraints and the nature of the heavy computation required.
Future Potential of Digital Twin Technology
The number of applications of digital twin technology across a plethora of industries is bound to grow exponentially over the next few years. Let’s find out how:
Exponential Market Growth
The global digital twin market is projected to experience explosive growth as technological advancements in IoT, AI, and 5G make the technology more accessible. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and automotive are expected to lead this growth, driven by their increasing demand for real-time data insights and predictive analytics. As costs decrease and platforms become user-friendly, even smaller businesses will adopt digital twin technology.
Digital Twins for Individual Consumers
The future may see digital twins tailored for individual consumers. For instance, in healthcare, personalized digital twins could simulate patient-specific treatments, predicting outcomes and optimizing care plans. In fitness, wearable devices might create digital replicas of users to track physical health and recommend improvements, pushing the boundaries of preventive healthcare.
Simulating at a Large Scale for Systemic Solutions
Here we dive deeper into how digital twin technology can be harnessed for positive impact, without ignoring the potential for misuse. This data can be used to build digital twins of ecosystems, weather patterns, and urban infrastructures, enabling policymakers to explore the impact of different responses, from cutting emissions to promoting urban mobility, and better advise decision-makers.
Integration with Quantum Computing and Blockchain
The convergence of digital twins with emerging technologies like quantum computing and blockchain solution is expected to unlock even greater potential. Quantum computing could enable faster and more complex simulations, while blockchain would enhance data security and transparency. For instance, combining blockchain with digita`l twins could maintain the secure tracking of assets in supply chains, providing an additional layer of trust and accountability.
Expansion into Space and Aerospace
Digital twins are already playing a role in space exploration, such as NASA’s use of twin technology for spacecraft and mission simulations. The future may see further advancements, with digital twins being used to optimize interplanetary travel, maintain space habitats, and simulate conditions on extraterrestrial bodies.
Mainstreaming Sustainability
In the future, digital twin technology will be more sustainable. Businesses will use digital twins to optimize how much energy they consume, cut down on waste, and create sustainable supply chains. Such endeavors also go a long way in achieving global sustainability goals, especially in energy-intensive sectors like manufacturing and construction.
Widespread Adoption Across Diverse Sectors
With digital twin platforms becoming increasingly versatile, their use will be pushed to sectors that have previously not fully adopted the technology. Aspects like this will lead to more innovative use cases for digital twins in various areas like agriculture (for precision farming), entertainment (for virtual reality), and education (for interactive learning environments) and many other areas in the coming years.
Conclusion
From next-level product development to sustainability, digital twin technology is certainly a game-changer for businesses. Adopting this technology can facilitate innovation, lower costs, and enhance decision-making for organizations. As these changes take effect, digital twins will reshape business dynamics and industry practices, leading us to a more intelligent, connected world.







 Blockchain
Blockchain Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Services
Infrastructure
Services Metaverse
Metaverse QA
Automation
QA
Automation UI/UX
UI/UX







